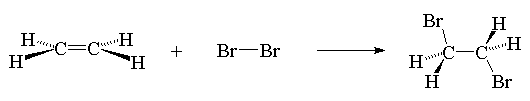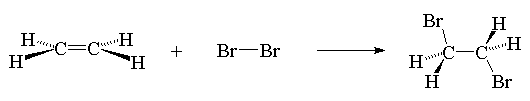INTRODUCTION
"Organic chemistry nowadays almost drives me mad.
To me it appears like a primeval tropical rain forest
full of the most remarkable things, a dreadful endless
jungle into which one does not dare enter for there
seems to be no way out"
Wöhler 1835
The aim of the Organic course is to give you an understanding of the:
- Basic organic chemical reactions and how they happen
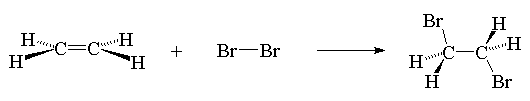
- Structures and shapes of organic molecules
- Spectroscopic methods for determination of organic structures
Definition of Organic Chemistry
- Organic chemistry deals with compounds in which carbon is the principal element
- Organic substances arise in all sorts of places - plants, animals, food, medicines, industry, research laboratories
- Every living organism made of organic chemicals
- 14 million organic substances - number increases by 10,000 per week!!
The Unique Nature of Carbon – Bonding in Organic Carbon
- Catenation - Carbon atoms can bond together to form
- Stable extended chains of atoms
- Rings
- Multiple bonds
- Carbon has atomic number = 6
- Electronic configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p2
- Valence of 4 – four bonds to completely fill outer electron shell of carbon
- Carbon forms bonds to
- Itself – single, double, triple
- Metals – Na, K, Fe, Cu, Mg …
- Heteroatoms – N, P, O, S, X (halogens)
- C-C and C-H bonds are strong
|
C-C |
356 kJ mol-1 |
|
C-H |
412 kJ mol-1 |
|
Si-Si |
176 kJ mol-1 |
|
N-N |
163 kJ mol-1 |
|
O-O |
146 kJ mol-1 |
|
I-I |
152 kJ mol-1 |
- C-C and C-H bonds are non-polar
- A combination of the strength and non-polar nature make C-C and C-H bonds unreactive
There are four experimentally observed bonding arrangements for carbon:
|
Type of bonds |
Hybridisation |
Geometry |
Examples |
|
4 single bonds |
sp3 |
Tetrahedral |
CH4, CH3CH3 |
|
2 single, 1 double bond |
sp2 |
Trigonal planar |
CH2=CH2, CH2=O |
|
1 single, 1 triple bond
2 double bonds |
sp |
Linear |
H-C º C-H
CH2=C=O |
Where it is important to represent the three-dimensional shape of a molecule, the following convention is adopted:
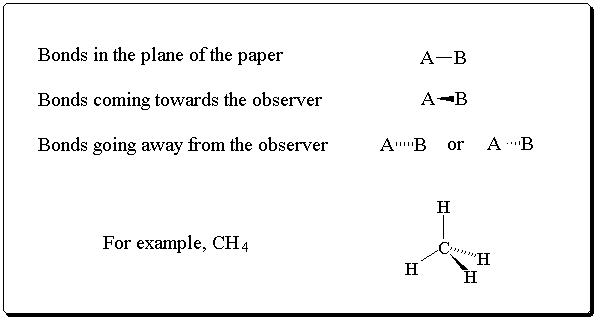
There are a number of ways that organic molecules can be drawn and it is important to become familiar with the different representations
Representation of Organic Molecules
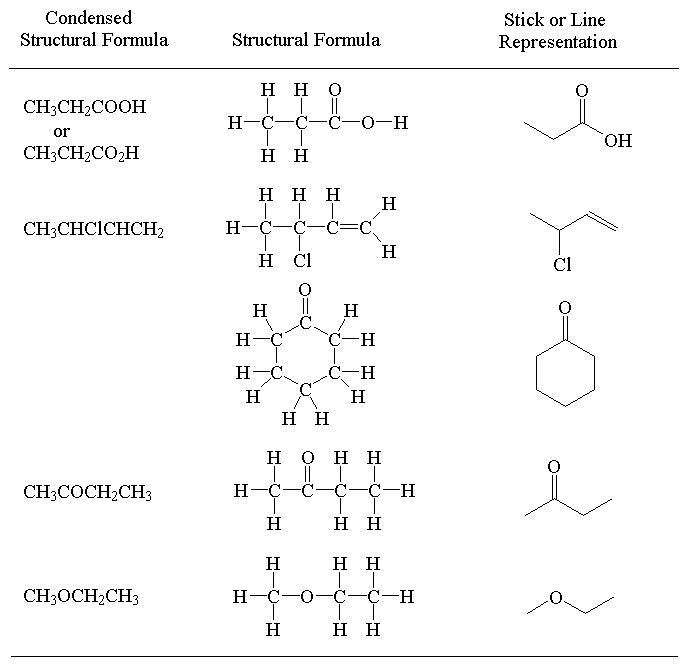
In the stick representation:
- Carbon atoms are not usually shown but assumed to be at the intersection of 2 or more bonds and at the end of each line.
- Hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon are not shown but the number determined as the number required to make the valence of carbon up to 4.
- Heteroatoms (O, N, F, Cl, B, I, S etc) are shown.
- When drawing neutral organic molecules:
- C always has a valence of 4
- N always has a valence of 3
- O always has a valence of 2
- X (halogen) always has a valence of 1
Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry
ºC and the polar bonds from carbon to heteroatoms are more reactive than C-C or C-H bonds and hence where the chemistry takes place. This part of the molecule is called the Functional Group.
An organic compound can be viewed as a backbone (skeleton) of carbon-carbon single bonds with other groups of atoms, functional groups, attached at various points.
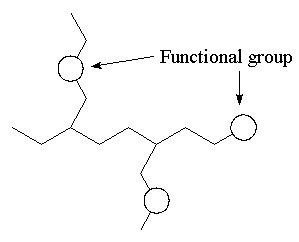
- The combination of the ability to form a vast range of unreactive carbon frameworks to which can be added special reactive sites gives the diversity of organic chemistry.
- Functional groups confer the characteristic chemical and physical properties of the compounds that contain them.
- Functional groups undergo the same chemical reactions irrespective of the type of molecule that contains them.
- A molecule containing several functional groups displays reactions that represents the sum of the reactions of each functional group.
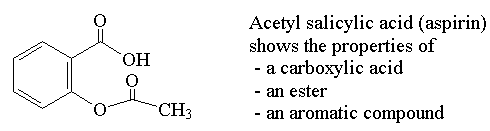
Functional Groups
Organic compounds are classified by Functional Groups, which are responsible for chemical behaviour. Functional groups are involved in naming organic compounds.
R is the general abbreviation for the "rest of the molecule".
|
Class name
|
General formula |
Examples |
|
alkane
|
RCH3 |
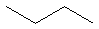 CH4 CH3CH2CH2CH3 CH4 CH3CH2CH2CH3
|
|
alkene
|
R2C=CR2 |
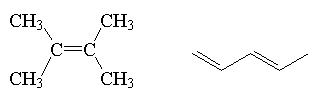 |
|
alkyne
|
RCº CR |
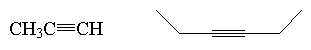 |
|
aromatic compound
(arene) |
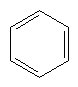
|
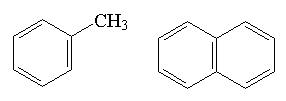 |
|
alcohol
|
R-OH |
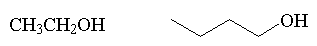
|
|
ether
|
R-O-R |

|
|
amine
|
R3N |
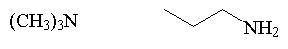
|
|
aldehyde
|
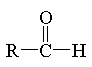
|
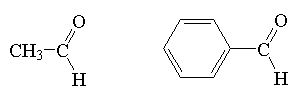 |
|
ketone
|
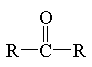
|
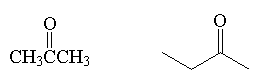 |
|
carboxylic acid
|
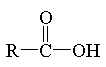
|
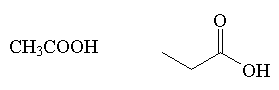 |
|
acid chloride
|
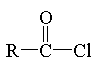
|
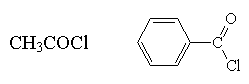 |
|
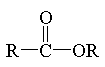
ester
|
|
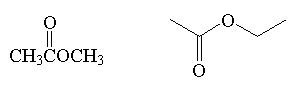 |
|
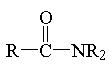
amide
|
|
 |
Questions on Functional Groups
Return to the Index