Why US elections are ranked worst among Western democracies
America is not a shining example for developing democracies, writes Professor Pippa Norris.

Donald Trump speaks at a campaign event in Fountain Hills, Arizona. Image: Wikimedia Commons/Gage Skidmore.
The world is currently transfixed by the spectacle of American elections.
From New York, London and Paris to Beijing, Moscow, and Sydney there is endless heated debate in the news media and across dinner tables about the factors fueling the remarkable success of Donald Trump, speculation about a brokered convention shattering the old GOP, and the most likely outcome of a polarising Trump-Clinton battle in the fall.
This contest matters. It is the election for the most powerful leader in the Western world, and some - like the Economist Intelligence Unit - regard Donald Trump as a major risk to global prosperity and stability. Also, as citizens of one of the world’s oldest democracies, Americans like to think that the United States provides an influential role model for how elections should run in other countries.
The Electoral Integrity Project (EIP), founded in 2012, provides an independent evaluation of the quality of elections worldwide. The EIP's results have been published in several books, including my own Why Electoral Integrity Matters and Why Elections Fail – books that focus on comparing the quality of elections, understanding why problems arise, and diagnosing what can be done about these flaws.
We can use the data collected by the EIP to ask: Is the US the electoral role model it imagines itself to be?
A democratic role model?
In practice, recent years have seen a long series of vulnerabilities in the conduct of American elections, as documented by the 2014 report of the bipartisan Presidential Commission on Election Administration. Indeed, these issues have been under close scrutiny ever since the notoriously flawed ballot design in Florida in 2000.
Since then, the Commission has reported wait times in excess of six hours to cast a ballot in Ohio, inaccurate state and local voter registers, insufficiently trained local poll workers, and the breakdown of voting machines in New York.
Standards remain uneven across the country. The Pew Center’s 2012 Election Performance Index, for instance, suggests that states such as North Dakota, Minnesota and Wisconsin performed relatively well against a range of quality indicators combining voting convenience and electoral integrity. Other states, including California, Oklahoma, and Mississippi demonstrated noticeable shortfalls.
Problems reported by the media
It was no different during the 2014 midterm elections. The news media reported a range of problems on polling day - some trivial, others more serious. It is unclear whether these arose from accidental administrative mistakes or intentional dirty tricks.
At least 18 state election websites were reported to have experienced disruptions on election day, preventing voters from using the sites to locate polling places and ballot information.
In Virginia, a State Department of Elections spokesman said that 32 electronic voting machines at 25 polling places experienced problems. In both Virginia and North Carolina, the Washington Post reported cases of electronic polling machines which recorded a vote for the Democratic candidate when the screen was touched to cast a vote for the Republican. And in Texas the statewide voter registration system crashed, forcing many to complete provisional ballots when poll workers were unable to confirm voter eligibility.
Meanwhile, new state laws requiring electors to present photo identification caused confusion in several states, including Texas, Georgia, and North Carolina.
These problems are not fading away.
During the 2016 primary in North Carolina, there was confusion about new photo ID requirements and long lines. Court decisions over voter identification laws currently remain pending in Texas and Virginia.
Problems of money in politics
As well as repeated procedural flaws, there has been speculation that public disgust with the role of money in politics, and the role of major donors in buying access to Congress, is one of the major factors driving the primary campaigns.
Much of Trump's visibility comes from exploiting his advantage in attracting free social media and spending less on TV airwaves than any other major candidate. He commonly claims that his organisation is more self-funded than most presidential campaigns, without support by a super-PAC. This may appeal to voters who are suspicious of the role of money in American elections and of the honesty of politicians who are seen to be in the pockets of rich donors and corporate interests.
Similarly, Bernie Sanders has campaigned on his ability to raise funds from multiple small donors. He claims Hillary Clinton has been more beholden to establishment donors and fat fees from corporate speaking engagements.
Suspicion of the role of money in politics seems to be widespread.
In the 2012 National Election Survey, for example, when the public was asked whether ‘Rich people buy elections', two-thirds of Americans agreed with this statement.
Comparing the US to other democracies
Some may be tempted to think headlines are exaggerating the true extent of any problems in America by highlighting negative cases which are actually fairly isolated.
Is there actually more systematic evidence suggesting that American elections are flawed? And how does the US compare with other long-standing democracies worldwide?
New evidence that gives insights into this issue has been gathered by the Electoral Integrity Project. This independent research project is funded by the Australian Research Council's Laureate award with a team of researchers based at the University of Sydney and Harvard University.
The 2015 annual Year in Election report compares the risks of flawed and failed elections, and looks at how well countries around the world meet international standards. The report gathers assessments from over 2000 experts to evaluate the perceived integrity of all 180 national parliamentary and presidential contests held between July 1, 2012 to December 31, 2015 in 139 countries worldwide. These include 54 national elections held last year.
Forty experts were asked to assess each election by answering 49 questions The overall 100-point Perceptions of Electoral Integrity (PEI) index is constructed by summing up the responses.
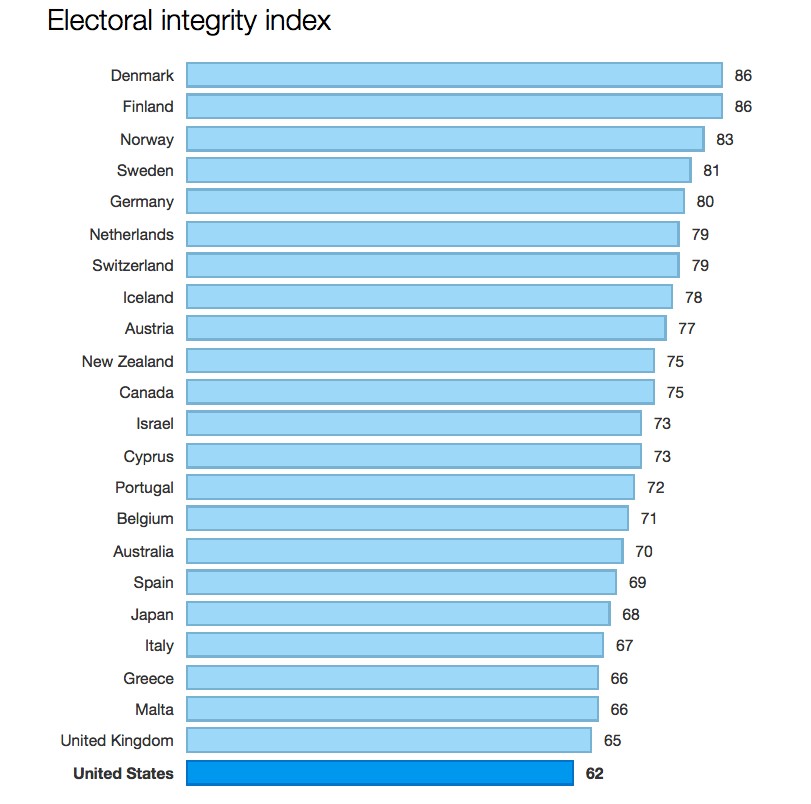
Data: Electoral Integrity Project.
This chart compares and contrasts the overall 100-point PEI index for all elections held since 2012 in the Western democracies covered in the survey. In the US, this covers both the 2012 presidential elections and the 2014 Congressional contests.
Americans often express pride in their democracy, yet the results indicate that domestic and international experts rate the US elections as the worst among all Western democracies.
Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden are at the top of the ranking, all scoring over 80 on the 100 point PEI Index. Several democracies from diverse regions and cultures – for example, Israel and Canada – are ranked in the middle of the pack.
But the US scores 62, a full 24 points lower than Denmark and Finland. The UK also performs fairly poorly, along with Greece and Australia. One reason for this is that proportional electoral systems – which translate votes into seats on a proportional basis – usually tend to score higher as they provide more inclusive opportunities for smaller parties. All of the Nordic countries, for example, use a proportional system.
Comparisons can also be drawn with all 180 parliamentary and presidential elections included in the latest report, covering 139 countries worldwide. The 2012 US presidential election ranks 60th out of 180 elections worldwide, close to Bulgaria, Mexico and Argentina.
This is no one-time shortcoming. The 2014 US Congressional elections rank even worse, 65th out of 180 worldwide.
By contrast, elections in many newer democracies are seen by experts to perform far better in the global comparison, such as in Lithuania (ranked 4th), Costa Rica (6th), and Slovenia (8th).
What stages of US elections are weakest?
What produces these results? To explore this issue, EIP also conducted a second survey with almost 200 experts to compare the performance of the 2014 congressional elections across 21 US states.
The results show that the worst problem across most states involved gerrymandering of district boundaries to favor incumbents. The mean score for American states was just 42 on a 100-point scale.
Other weaknesses concerned whether electoral laws were unfair to smaller parties like the Green Party, favored the governing party, or restricted voter’s rights.
Campaign finance – for example, whether parties and candidates had equitable access to public subsidies and political donations – was also seen by experts as a problem.
Finally voter registration was also viewed critically. Issues here included whether the register itself was accurate with, in some cases, citizens not listed and, in others, ineligible electors registered.
By contrast, voting processes were rated more favorably. Factors here included whether any fraudulent votes were cast, whether the voting process was easy, whether voters were offered a genuine choice at the ballot box, along with the vote count and post-election results. These last two measures each received a high score of 85.
Much debate in the US focuses upon potential risks of fraud or voter suppression at the ballot box, but in fact experts rate earlier stages of American elections more critically.
Why are American elections so bad?
Why are American elections particularly vulnerable to these sorts of problems? It is a complex story.
In my book, Why Elections Fail, I argue that a large part of the blame can be laid at the door of the degree of decentralisation and partisanship in American electoral administration. Key decisions about the rules of the game are left to local and state officials with a major stake in the outcome. For example, gerrymandering arises from leaving the processes of redistricting in the hands of state politicians, rather than more impartial judicial bodies.
Moreover, the role of money in American campaigns has become progressively deregulated in recent decades, thanks in part to the Citizens United Supreme Court decision, while election costs have spiraled. Add to that the fuel of an inflammatory campaign by Donald Trump, and the prospects for agreement about the outcome of the election become more remote.
Pippa Norris is an ARC Laureate Fellow and Professor of Government and International Relations at the University of Sydney and McGuire Lecturer in Comparative Politics at Harvard Unversity. This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.
